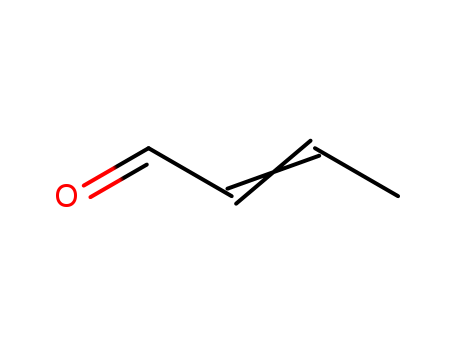
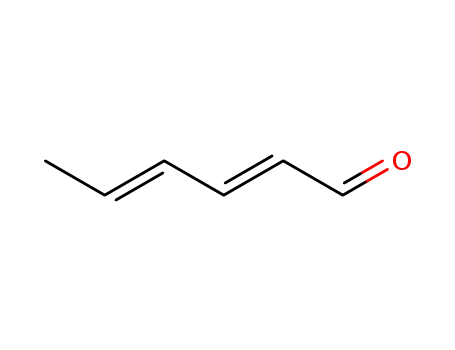Buy Quality Crotonaldehyde 123-73-9 In Stock with Immediately Delivery
- Molecular Formula:C4H6O
- Molecular Weight:70.091
- Appearance/Colour:clear liquid
- Vapor Pressure:32 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- Melting Point:- 76 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:n20/D 1.437
- Boiling Point:104 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:4.6 °C
- PSA:17.07000
- Density:0.819 g/cm3
- LogP:0.76140
Crotonaldehyde(Cas 123-73-9) Usage
|
Chemical Description
|
Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound typically sold as a mixture of E- and Z-isomers, with the E-isomer being more common. Hebei KuiSheng Trading Co., LTD ,a company specializing in the production and supply of chemicals for various industries. we take pride in our ability to carefully formulate chemicals that meet the highest standards of quality, efficiency, and safety. Through advanced technology and strict quality control measures, we ensure that our products consistently deliver exceptional performance and reliability. Whether you are in need of chemicals for pharmaceutical, agricultural, or industrial applications, we offer a wide range of solutions to meet your specific requirements. Our team is dedicated to providing excellent customer service and we strongly believe in establishing long-lasting business relationships built on trust and mutual success. |
|
Air & Water Reactions
|
Highly flammable.
|
|
Uses
|
It is primarily used in the production of sorbic acid, a preservative that inhibits yeast and mold growth. Crotonaldehyde also serves various industrial purposes, such as a warning agent in fuels, an alcohol denaturant, a stabilizer for tetraethyl-lead, and in the preparation of rubber accelerators and leather tanning agents. It is highly flammable, reacts violently with strong oxidizers, and can polymerize dangerously in certain conditions. Crotonaldehyde is severely irritating to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, and inhalation can cause respiratory distress and pulmonary edema. Despite its toxic nature, it is widely used in the manufacture of plastics, rubber, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial products. Handling crotonaldehyde requires careful safety precautions due to its reactivity and health hazards. |
InChI:InChI=1/C8H14O4/c1-3-7(9)11-5-6-12-8(10)4-2/h3-6H2,1-2H3
Allow me to outline some of our key advantages: 1. High quality with competitive prices: We strive to offer chemicals of the highest quality while remaining competitive in the market. 2. All purity >99%: Our products undergo rigorous purification processes to guarantee high purity levels. 3. Manufacturer with factory prices: As a manufacturer, we have the ability to offer high-quality products at competitive factory prices. 4. Fast and safe delivery: We understand the importance of timely and secure deliveries. Therefore, we have established reliable logistics networks to ensure efficient transportation of our products. 5. OEM is welcome: We are open to providing Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) services, allowing you to customize products according to your specific needs. 6. Sufficient stock: Our extensive inventory ensures that we can fulfill orders promptly, regardless of their size or complexity. We are confident that with our extensive experience and dedication to excellence, we can be your trusted partner in chemical solutions. We would greatly appreciate the opportunity to work with you and contribute to the success of your business. Should you require any further information or have specific inquiries, please do not hesitate to contact us. We look forward to hearing from you.
123-73-9 Relevant articles
Structure Sensitivity of the Hydrogenation of Crotonaldehyde over Pt/SiO2and Pt/TiO2
Martin Englisch a , Andreas Jentys b , Johannes A. Lercher a 1
, Journal of Catalysis Volume 166, Issue 1 , February 1997, Pages 25-35
Hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde has been studied over SiO2- and TiO2-supported Pt catalysts. Over Pt/SiO2, the selectivity to the primary products butyraldehyde and crotylalcohol depends critically on the Pt particle size; i.e., the selectivity to the unsaturated alcohol increases with increasing particle size. For large metal particles, the high fraction of Pt(111) surfaces is concluded to favor the adsorption of crotonaldehyde via the carbonyl bond. On small Pt particles, the high abundance of metal atoms in low coordination allows unconstrained adsorption of both double bonds.
Magnetic core-shell Fe3O4?Cu2O and Fe3O4?Cu2O-Cu materials as catalysts for aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols assisted by TEMPO and: N -methylimidazole
Liu, Xiaoming,Lu, Chunxin,Senthilkumar, Samuthirarajan,Shen, Zhongquan,Xu, Binyu,Zhong, Wei
, p. 26142 - 26150 (2020)
In this work, core-shell Fe3O4?Cu2O and ...
Adsorption and thermal chemistry of acrolein and crotonaldehyde on Pt(111) surfaces
Juan Carlos de Jesús , Francisco Zaera
, Surface Science Volume 430, Issues 1–3 , 21 June 1999, Pages 99-115
The RAIRS data indicate that while acrolein initially adsorbs with its plane parallel to the surface and interacts mainly via the carbonyl group, crotonaldehyde adopts a more complex geometry where the main interaction to the metal is via a rehybridization of the CC double bond. It is suggested here that the changes in adsorption geometry induced by substitutions in the CC double bond may be responsible for the observed changes in the subsequent reactivity of the adsorbed unsaturated aldehydes.
Kinetics and Mechanism of Electron Transfer Reactions: Oxidation of Crotyl Alcohol by Peroxomonosulfate in Aqueous Acidic Medium
Sharma, Priyamvada,Sailani, Riya,Meena, Anita,Khandelwal
, p. 335 - 342 (2018)
The kinetics and mechanism of oxidation ...
123-73-9 Upstream products
123-73-9 Downstream products